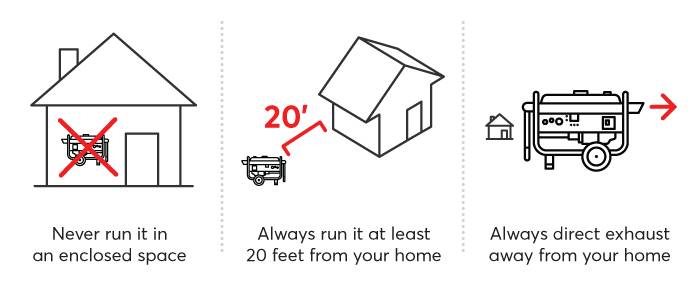
Whole House Generators
Power Outages happen at any time… be secure that you will have safety, comfort and convenience with an easy-to-use generator and 24/7 protection. Our electricians will work with you to select the best model for your residential or commercial needs. Never lose power again!